
As of Wednesday, January 15, Microsoft will make the non-beta version of its new, Chromium-based version of the Edge browser to Windows 10 Home and Pro users. We covered the beta version of Chromium-based Edge in November. The beta was still pretty raw then—but 'raw' is a relative term. The new Edge project began with a complete and fully functional Web browser—Chromium—so it worked fine for browsing the Web. There were just a few rough edges as far as installing extensions, logging into them, and the like.
- Then, use the driver.capabilities'browserVersion' command to get the Microsoft Edge Chromium version in python, more detail, please check the following code (remember to change the path to yours).
- The Microsoft Edge browser for business has powerful search features, productivity tools, privacy and security controls, and more. Start piloting today.
We've seen one take waxing nostalgic for the old, purely Microsoft developed version of Edge, but we don't think many people will miss it much. It's not so much that Edge was a bad browser, per se—it just didn't serve much of a purpose. Edge didn't have the breadth of extensions or the user-base enthusiasm of Chrome or Firefox—and it was no better than they are at running crusty old 'Internet Explorer Only' websites and Web apps.
While there is some validity to worrying about one company 'controlling the Web' and one of Google's biggest competitors now becoming a Google downstream, we don't think those concerns add up to much. We don't want to see the full-on Google Chrome become any more indispensable than it already is—but we don't think Microsoft trading in its own fully proprietary, closed-source HTML-rendering engine for one of the two biggest open source rendering engines is a bad thing.
We adopted the Chromium open source project in the development of Microsoft Edge to create better web compatibility for our customers, and less fragmentation of the web for all web developers. We are continuing our commitment to be an active contributor to the Chromium project.
We downloaded the final beta version of Chromium-based Edge—the one available on the afternoon of the 14th, one day before the official launch—and took it for a spin in a Windows 10 virtual machine. Mostly, it still just looks like a slightly plainer version of Chrome—which isn't a bad thing! Sites load snappily, UI elements are familiar, and so forth. One of the biggest obvious improvements since the last time we test-drove Chromium Edge is the ability to install extensions from the official Chrome Web store.
AdvertisementMicrosoft's own Web store is still extremely sparse—we went looking for the must-have, EFF-developed HTTPS Everywhere, and instead we got a recommendation for 'NBC Sports'—which does not seem well-loved by its users. However, typing 'chrome Web store' in the address/search bar took us right where we needed to go and presented us with an obvious tool-tip for installing third-party extensions. That was that—HTTPS Everywhere installed with a single click, just as you'd expect it to on Chromium or Google Chrome itself.
Chromium-based Edge is still missing a couple of obvious features to compete with the full Google Chrome experience—most notably, browser history and extensions don't sync between devices yet. This is described as a temporary problem in the 'Known Issues' page, and it may even be fixed already in the production version launching today.
Pushing the new Edge as something to look forward to right now is difficult—we suspect most people who really care about their browser will continue using Chrome, Firefox, or whatever less-well-known variant they've found and learned to love. Meanwhile, the people who have actually been actively using Edge likely won't notice much of a change—unless Microsoft bobbles something in the user data import functionality when they push the official, non-beta version out through Windows Update later this month.
In all likelihood, the change absolutely will improve the lives of the folks who 'just click the blue E' in the long run, though. It will likely make it easier for Microsoft to lure more technical users—who demand feature and extension parity but might be interested in Edge's Azure authentication back-end—away from Google Chrome.
This article initially stated that Chromium-based Edge was being pushed over Windows Update beginning on the 15th; a Microsoft representative reached out to correct us: it was only available for download beginning on the 15th, and will not be pushed over Windows Update until later this month. The article has been updated accordingly.
-->Use the following information to configure Microsoft Edge policy settings on your Windows devices.
Note
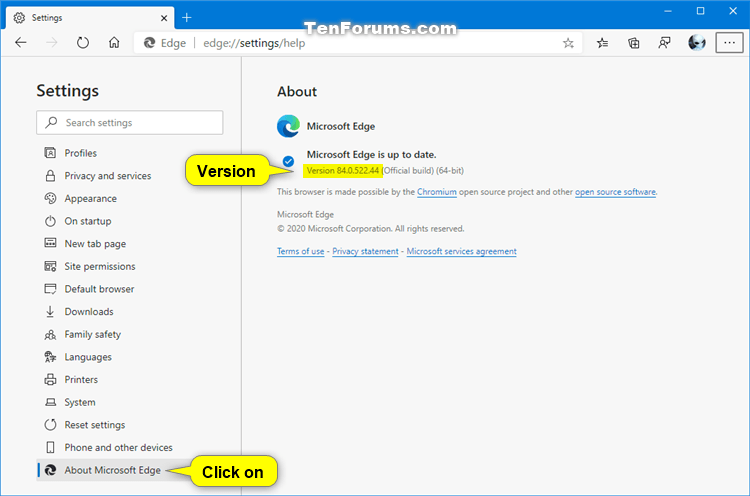
This article applies to Microsoft Edge version 77 or later.
Configure policy settings on Windows
You can use group policy objects (GPO) to configure policy settings for Microsoft Edge and managed Microsoft Edge updates on all versions of Windows. You can also provision policy through the registry for Windows devices that are joined to a Microsoft Active Directory domain, or Windows 10 Pro or Enterprise instances enrolled for device management in Microsoft Intune. To configure Microsoft Edge with group policy objects, you install administrative templates that add rules and settings for Microsoft Edge to the group policy Central Store in your Active Directory domain or to the Policy Definition template folder on individual computers and then configure the specific policies you want to set.
You can use Active Directory group policy to configure Microsoft Edge policy settings if you prefer to manage policy at the domain level. This enables you to manage policy settings globally, targeting different policy settings to specific OUs, or using WMI filters to apply settings only to users or computers returned by a particular query. If you want to configure policy on individual computers, you can apply policy settings that only affect the local device using the Local Group Policy Editor on the target computer.
Microsoft Edge supports both mandatory and recommended policies. Mandatory policies override user preferences and prevents the user from changing it, while recommended policy provide a default setting that may be overridden by the user. Most policies are mandatory only; a subset are mandatory and recommended. If both versions of a policy are set, the mandatory setting takes precedence. A recommended policy only takes effect when the user has not modified the setting.
Tip
You can use Microsoft Intune to configure Microsoft Edge policy settings. For more information, see Configure Microsoft Edge using Microsoft Intune.
There are two administrative templates for Microsoft Edge, both of which can be applied either at the computer or Active Directory domain level:
- msedge.admx to configure Microsoft Edge settings
- msedgeupdate.admx to manage Microsoft Edge updates.
To get started, download and install the Microsoft Edge administrative template.
1. Download and install the Microsoft Edge administrative template
If you want to configure Microsoft Edge policy settings in Active Directory, download the files to a network location you can access from a domain controller or a workstation with the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) installed. To configure on an individual computer, simply download the files to that computer.
When you add the administrative template files to the appropriate location, Microsoft Edge policy settings are immediately available in the Group Policy Editor.
Go to the Microsoft Edge Enterprise landing page to download the Microsoft Edge policy templates file (MicrosoftEdgePolicyTemplates.cab) and extract the contents.

Add the administrative template to Active Directory
On a domain controller or workstation with RSAT, browse to the PolicyDefinition folder (also known as the Central Store) on any domain controller for your domain. For older versions of Windows Server, you may need to create the PolicyDefinition folder. For more information, see How to create and manage the Central Store for Group Policy Administrative Templates in Windows.
Open MicrosoftEdgePolicyTemplates and go to windows > admx.
Copy the msedge.admx file to the PolicyDefinition folder. (Example: %systemroot%sysvoldomainpoliciesPolicyDefinitions)
In the admx folder, open the appropriate language folder. For example, if you’re in the U.S., open the en-US folder.
Copy the msedge.adml file to the matching language folder in the PolicyDefinition folder. Create the folder if it does not already exist. (Example: %systemroot%sysvoldomainpoliciesPolicyDefinitionsEN-US)
If your domain has more than one domain controller, the new ADMX files will be replicated to them at the next domain replication interval.
To confirm the files loaded correctly, open the Group Policy Management Editor from Windows Administrative Tools and expand Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Microsoft Edge. You should see one or more Microsoft Edge nodes as shown below.
Add the administrative template to an individual computer

Get Edge Chromium
- On the target computer, open MicrosoftEdgePolicyTemplates and go to windows > admx.
- Copy the msedge.admx file to your Policy Definition template folder. (Example: C:WindowsPolicyDefinitions)
- In the admx folder, open the appropriate language folder. For example, if you’re in the U.S., open the en-US folder.
- Copy the msedge.adml file to the matching language folder in your Policy Definition folder. (Example: C:WindowsPolicyDefinitionsen-US)
- To confirm the files loaded correctly either open Local Group Policy Editor directly (Windows key + R and enter gpedit.msc) or open MMC and load the Local Group Policy Editor snap-in. If an error occurs, it’s usually because the files are in an incorrect location.
2. Set mandatory or recommended policies
You can set mandatory or recommended policies to configure Microsoft Edge with the Group Policy Editor for both Active Directory and individual computers. You can scope policy settings to either the Computer Configuration or User Configuration by selecting the appropriate node as described below.
To configure a mandatory policy, open the Group Policy Editor and go to (Computer Configuration or User Configuration) > Policies > Administrative Templates > Microsoft Edge.
To configure a recommended policy, open the Group Policy Editor and go to (Computer Configuration or User Configuration) > Policies > Administrative Templates > Microsoft Edge – Default Settings (users can override).
3. Test your policies
Get Edge Chromium Offline Installer
On a target client device, open Microsoft Edge and navigate to edge://policy to see all policies that are applied. If you applied policy settings on the local computer, policies should appear immediately. You may need to close and reopen Microsoft Edge if it was open while you were configuring policy settings.
For Active Directory group policy settings, policy settings are propagated to domain computers at a regular interval defined by your domain administrator, and target computers may not receive policy updates right away. To manually refresh Active Directory group policy settings on a target computer, execute the following command from a command prompt or PowerShell session on the target computer:
You may need to close and reopen Microsoft Edge before the new policies appear.
You can also use REGEDIT.exe on a target computer to view the registry settings that store group policy settings. These settings are located at the registry path HKLMSOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftEdge.

See also
